Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tsuda, Takashi; Kurita, Genichi; Fujita, Takaaki
Journal of Plasma Physics, 72(6), p.1149 - 1152, 2006/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:10.78(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The current density is expected to be negative in the central region of the tokamak when the amplitude of bootstrap current or off-axis current drive is large enough and a negative one-turn voltage exists. However, a flat current profile with almost zero value has been observed in experiments. The current profile with Current Hole has a tendency to be unstable to double tearing mode and we investigate the role of double tearing mode on the formation of Current Hole with RMHD simulation.
Tsuda, Takashi; Kurita, Genichi; Fujita, Takaaki
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 49, p.S83 - S86, 2006/12
The current density is expected to be negative in the central region of the tokamak when the amplitude of bootstrap current or off-axis current drive is large enough. However, a flat current profile with almost zero value has been observed in experiments even under the situation with negative one-turn voltage exists in the central region of plasma. Double tearing mode (DTM) can be unstable for the current profile with a "current hole" and some MHD activities are observed in JET before the formation of the current hole. On the contrary, no MHD activity is observed in the JT-60 experiment. Here, we study the condition of appearance of DTM and investigate the stability of DTM and the interaction between DTM (n=1 perturbation) and "Current Hole" with resistive RMHD simulations.
Matsumoto, Taro; Naito, Hiroshi*; Tokuda, Shinji; Kishimoto, Yasuaki*
Nuclear Fusion, 45(11), p.1264 - 1270, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:43.63(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A gyrokinetic particle simulation is executed to clarify the effect of the electron inertia on the MHD phenomena in the reversed shear configuration (RSC) of a cylindrical tokamak plasma. It is found that the collisionless (kinetic) double tearing modes grow up at the Alfv n time scale, and nonlinearly induce the internal collapse when the helical flux at the magnetic axis is less than that at the outer resonant surface. After the internal collapse, the secondary reconnection is induced by the current concentration due to the
n time scale, and nonlinearly induce the internal collapse when the helical flux at the magnetic axis is less than that at the outer resonant surface. After the internal collapse, the secondary reconnection is induced by the current concentration due to the 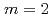 convective flow. It is also clarified that a nonlinear dynamics accompanied with the elementary processes caused by the
convective flow. It is also clarified that a nonlinear dynamics accompanied with the elementary processes caused by the 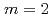 flow can generate a new RSC with resonant surfaces. In the presence of the density gradient, after the full reconnection induced by the
flow can generate a new RSC with resonant surfaces. In the presence of the density gradient, after the full reconnection induced by the 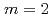 mode, the radial electric field is found to be generated due to the difference of the
mode, the radial electric field is found to be generated due to the difference of the 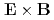 motion between ions and electrons. However, the intensity of the radial field is not so large as that induced by the collisionless kink mode.
motion between ions and electrons. However, the intensity of the radial field is not so large as that induced by the collisionless kink mode.
Matsumoto, Taro; Naito, Hiroshi*; Tokuda, Shinji; Kishimoto, Yasuaki
Physics of Plasmas, 12(9), p.092505_1 - 092505_7, 2005/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.86(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The behavior of the collisionless magnetohydrodynamics modes is investigated by the gyro-kinetic particle simulation in a cylindrical tokamak plasma in the parameter region where the effects of electron inertia and electron parallel compressibility are competitive for magnetic reconnection. Although the linear growth of the 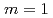 internal kink-tearing mode is dominated by the electron inertia, it is found that the growth rate can be nonlinearly accelerated due to the electron parallel compressibility proportional to the ion sound Larmor radius
internal kink-tearing mode is dominated by the electron inertia, it is found that the growth rate can be nonlinearly accelerated due to the electron parallel compressibility proportional to the ion sound Larmor radius 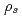 . It is also found that, as decreasing the electron skin depth
. It is also found that, as decreasing the electron skin depth 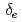 , the maximum growth rate before the internal collapse saturates independently of the microscopic scales such as
, the maximum growth rate before the internal collapse saturates independently of the microscopic scales such as 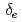 and
and 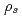 . The acceleration of growth rate is also observed in the nonlinear phase of the
. The acceleration of growth rate is also observed in the nonlinear phase of the 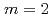 double tearing mode.
double tearing mode.
Kishimoto, Yasuaki
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 80(5), p.390 - 395, 2004/05
High performance magnetically confined plasma is realized by having structures in plasmas, where different elementary processes with different time and spatial scales are deeply contributing with each other. A research based on large scale simulation is then essential to understand such hierarchical complex plasmas. We discuss the underlying physical process of the structural plasma and present a prospect for future numerical simulations covering a wide dynamical range.
Matsumoto, Taro; Tokuda, Shinji; Kishimoto, Yasuaki; Naito, Hiroshi*
Physics of Plasmas, 10(1), p.195 - 203, 2003/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:16.93(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Effects of density gradient on the collisionless m=1 internal kink mode in a cylindrical tokamak plasma are studied by the gyro-kinetic particle simulations. When the density gradient is not large enough to change the full reconnection process, the phenomena after the full reconnection, such as the secondary reconnection and the evolution of the safety factor profile, are changed considerably due to the self-generated radial electric field, i.e. the m=0 mode. The growing mechanism is explained by the difference of 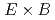 drift motion between ions and electrons, which is caused by the fast parallel motion of electron. Once the radial electric field is triggered by the symmetrical flow induced by the m=1 mode, the m=0 mode grows up to the same level as the m=1 mode, and drives an
drift motion between ions and electrons, which is caused by the fast parallel motion of electron. Once the radial electric field is triggered by the symmetrical flow induced by the m=1 mode, the m=0 mode grows up to the same level as the m=1 mode, and drives an 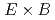 plasma rotation in the ion diamagnetic direction, which breaks the symmetrical plasma flow induced by the m=1 mode. The density and current distributions, and minimum safety factor after the full reconnection, are found to be affected by the asymmetrical flow driven by the m=1 and m=0 modes.
plasma rotation in the ion diamagnetic direction, which breaks the symmetrical plasma flow induced by the m=1 mode. The density and current distributions, and minimum safety factor after the full reconnection, are found to be affected by the asymmetrical flow driven by the m=1 and m=0 modes.
Takase, Kazuyuki; M.Z.Hasan*
16th IEEE/NPSS Symp. on Fusion Engineering (SOFE '95), 2, p.1538 - 1541, 1995/00
no abstracts in English
Takeda, Tatsuoki; Tani, Keiji; Tsunematsu, Toshihide; Kishimoto, Yasuaki; ; *; *
Parallel Computing, 18, p.743 - 765, 1992/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:48.33(Computer Science, Theory & Methods)no abstracts in English
Kunugi, Tomoaki; M.S.Tillack*; M.A.Abdou*
Fusion Technology, 19, p.1000 - 1005, 1991/05
no abstracts in English
Takeda, Tatsuoki; Tsunematsu, Toshihide; ; ;
Computational Mechanics 86;Theory and Applications, p.9 - 3, 1986/00
no abstracts in English
JAERI-M 9944, 28 Pages, 1982/02
no abstracts in English
; Tsunematsu, Toshihide; ; ; ; ; ; *; *; Takeda, Tatsuoki
JAERI-M 9354, 76 Pages, 1981/02
no abstracts in English